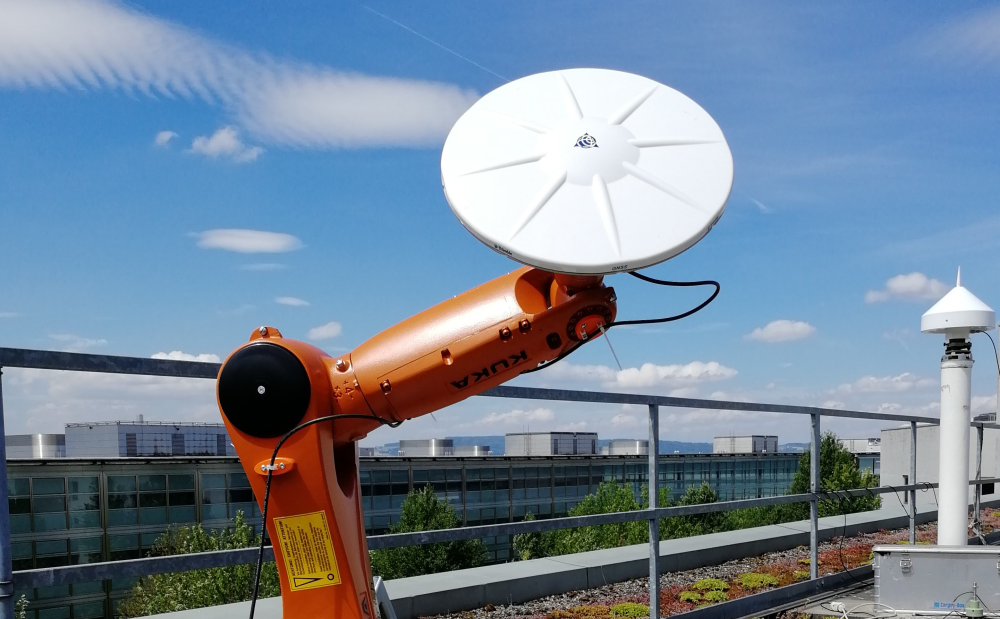
High-precision GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) play a major role in modern geodesy. Nowadays, we are confronted with four major systems and a variety of navigation signals. For scientific purposes, a combined, fully consistent and highly accurate analysis of tracking data from all available GNSS is essential. In addition more and more applications call for results available in (near) real time. We develop highly sophisticated analysis algorithms and schemes, which let us push the limits of detectable effects and signals in GNSS time series to an unprecedented level.
Project list:
GNSS Antenna Phase Center Calibration
The calibration of the phase centers of the most important antenna types for all GNSS constellations and for all frequencies used by these GNSS is an absolute necessity for high-accuracy GNSS positioning using multi-GNSS and multi-frequency antennas and receivers. Especially the realization of a highly stable and accurate reference frame, as the metrological basis for very challenging applications such as sea level rise, requires long time series of GNSS station coordinates computed with utmost accuracy and reliability. As a consistent set of antenna phase center calibrations for all major ground antenna types used in high-precision GNSS is essential, we took up this challenge and developed a method based on triple-differences for absolute antenna phase center calibrations. Results are regularly compared and discussed in a small group consisting of ESA ESOC (Darmstadt), Landesamt für Digitalisierung, Breitband und Vermessung (Munich), Geodetic Institute of the University of Bonn (Bonn) and ETH Zurich.
Start date:
01.01.2020
Project partners:
ESA, Frauenhofer Institute, LVDI
Contacts at MPG:
Markus Rothacher ()
Gregor Möller ()
Links:
-

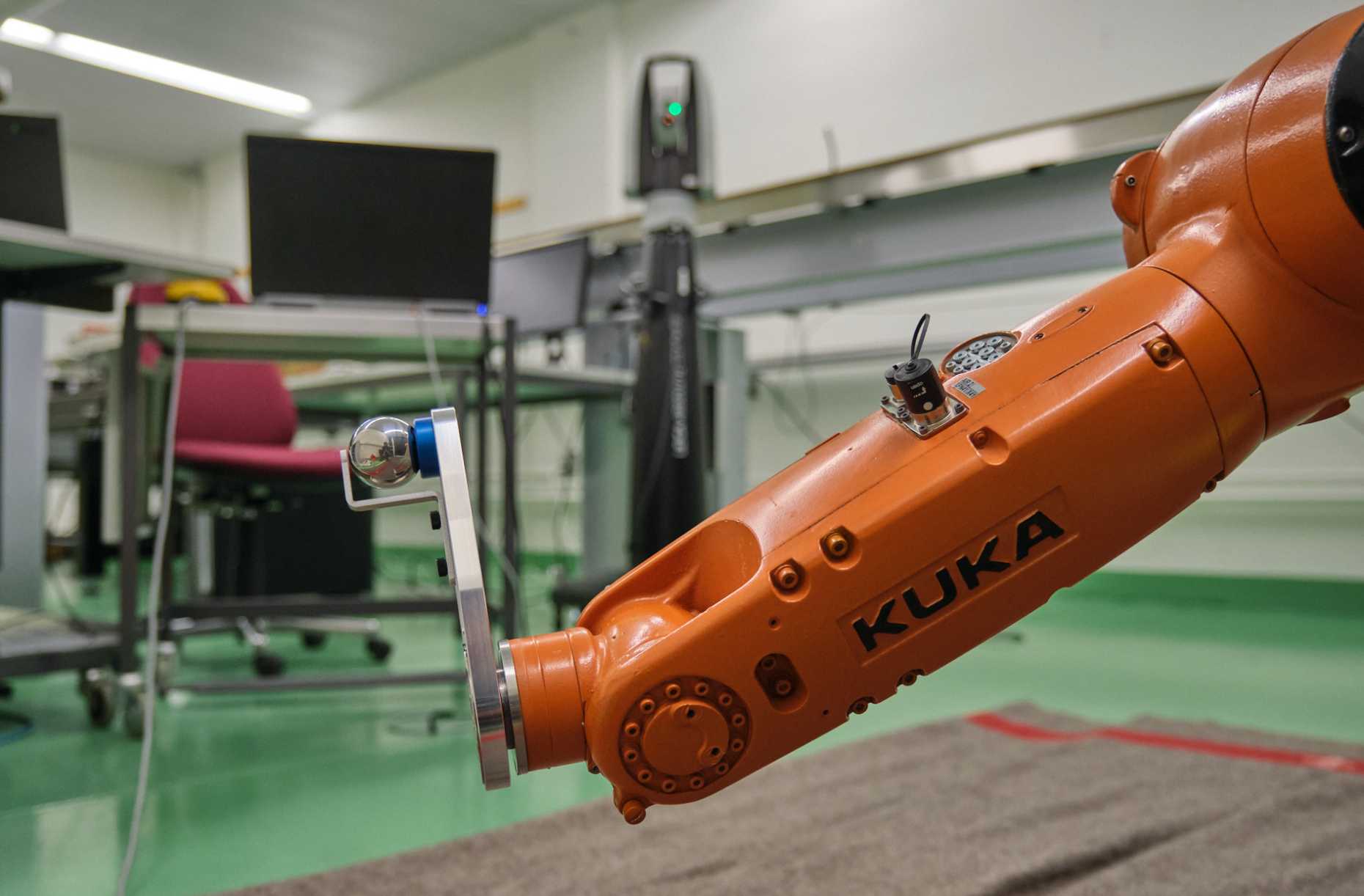
Calibration of the Kuka robot performance with a Laser Tracking System
The goal of this project is to calibrate the KUKA KR6 R900 sixx industrial robot for a wide variety of applications that require an absolute positioning accuracy of up to 0.1mm. Furthermore, the repeatability and accuracy in static and dynamic scenarios shall be evaluated. A laser tracker with absolute distance measuring capability is used to obtain highly accurate observations of the end effector position. Apart from geometric deviations from the nominal dimensions of the robot, the mechanical design of the joints is identified and a calibration model for a series of static and kinematic applications is derived.
Start date:
01.09.2020
Project partners:
ETH Zürich IGP
Contacts at MPG:
Gregor Möller ()
Markus Rothacher (ch)
Links:
-

CAMALIOT - AppliCation of machine learning technology for GNSS IoT data fusion
The rapid increasing number of mobile devices offer great potential for GNSS science exploitations, with unprecedented spatio-temporal resolution. The project CAMALIOT, will address these issues in order to increase the usability of IoT GNSS data for scientific purposes. It encompasses the whole pipeline from collecting raw IoT GNSS data, developing methods for efficiently and automatically processing them, to finally demonstrate their suitability for scientific applications
Start date:
02.03.2021
Project partners:
ETH Zürich IGP, IIASA
Contacts at MPG:
Benedikt Soja ()
Grzegorz Kłopotek ()
Markus Rothacher ()
Financiers (external):
ESA NAVISP
Links:
-